What Are AI Agents? Understanding Their Analytical Capabilities and Applications
Blog / What Are AI Agents? Understanding Their Analytical Capabilities and Applications
Have you come across the term “AI Agent” on social media or in tech news and wondered how artificial intelligence can autonomously handle complex tasks? More intriguingly, how can AI agents analyze data and make decisions without direct human supervision?
In this article, OneAsia takes you through what AI agents are, how they work in practice, and the key technologies behind them. By understanding their core principles and distinctions, you’ll gain a comprehensive view of this emerging field, and how AI agents are shaping the future across industries.
What Is an AI Agent? A Look at Its Core Mechanisms
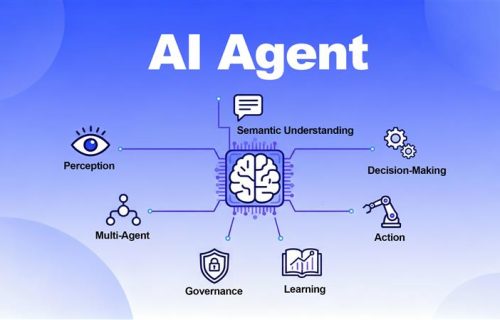
AI agent is an intelligent system capable of autonomous perception, decision-making, and execution. Within a given environment, it can analyze information, devise strategies, and carry out actions, which marks a major step toward self-directed AI.
Think of a virtual assistant that proactively checks your schedule, reminds you of meetings, and automatically adjusts appointments when something unexpected occurs. An AI agent functions in a similar way: it coordinates strategies, learns continuously, and improves collaboration accuracy over time.
From a technical perspective, an AI agent can be broken down into seven key components:
1. Perception
Through environmental sensing, an AI agent leverages large language models (LLMs) as its “intelligent core,” similar to how the human brain processes information. It can understand language and commands while integrating data from various sources, such as sensors, APIs, or databases to gain context and structure for more advanced decision-making.
2. Semantic Understanding & Goal Encoding
Using an LLM as its foundation, the AI agent interprets the meaning and intent behind input data, then translates those insights into actionable objectives. This allows it to break down tasks, allocate resources efficiently, and plan subsequent actions.
3. Decision-making & Planning
At its heart, an AI agent specializes in autonomous planning and task decomposition. Through machine learning, deep learning, and algorithmic modeling, it analyzes the task environment, divides complex goals into smaller subtasks, and computes optimal solutions. With real-time updates from the perception phase, the agent dynamically refines its strategies and decisions.
4. Action & Integration
Beyond passive responses, AI agents can actively initiate actions via external system APIs, such as retrieving online information, sending emails, or assigning tasks. Today’s agents already integrate seamlessly with enterprise systems like ERP and CRM, enabling smooth cross-platform collaboration and efficient workflow execution in dynamic environments.
5. Learning & Feedback
“Learning from the past to improve the future” captures the essence of AI agent optimization. By continuously reviewing historical data and user feedback, the agent identifies valuable patterns, updates its models, and enhances future task performance, creating a continuous improvement loop.
6. Governance & Sercurity
To ensure safe, compliant, and controllable operation, governance and security are critical. AI agents must verify that their data sources meet legal and ethical standards and comply with privacy and enterprise policies. Since agents often have high-level system permissions, multi-layer authentication and access controls are essential to prevent breaches and maintain data integrity.
7. Multi-Agent Systems (MAS)
Advanced AI frameworks support multi-agent collaboration, where several agents can share data, divide tasks, and make coordinated decisions in real time. These systems allow agents to communicate and assist each other, working together to solve large and complex challenges. This level of coordination forms the foundation of enterprise-level AI ecosystems that are connected, adaptive, and intelligent.
AI Agents vs. Agentic AI
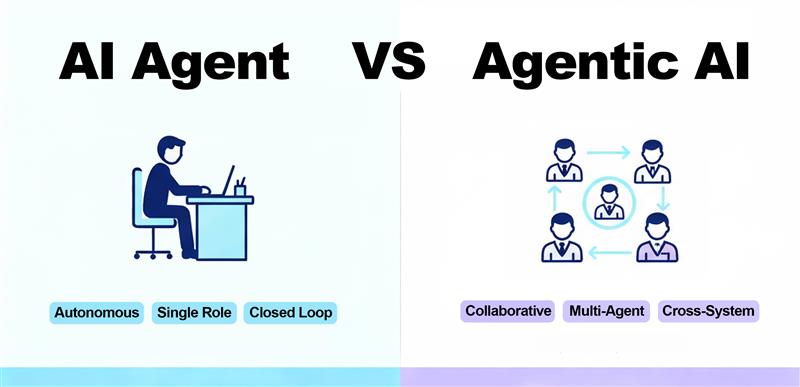
Now that we understand how AI agents work, let’s distinguish between AI agents and Agentic AI.
An AI agent typically refers to a self-contained intelligent entity capable of completing the full cycle of perception, decision-making, action, and learning autonomously, operating as a standalone unit.
In contrast, Agentic AI is a system-level architecture — a coordinated network of multiple agents and external tools working together. It focuses on multi-stage task planning and collaborative execution, integrating diverse systems to tackle more complex scenarios.
Comparison Between AI Agents and Agentic AI:
| Category | AI Agent | Agentic AI |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | A single intelligent technology capable of the full cycle of perception → decision-making → action → learning | A system-level architecture that integrates external tools and coordinates multiple agents |
| Key Characteristics | Strong autonomy, capable of independently completing specific or bounded tasks | Task-oriented, emphasizing cross-system integration and collaboration |
| Scope of Operation | Functions as an individual role | Operates across end-to-end workflows through multi-agent cooperation |
| Enterprise Analogy | A personal assistant | An entire administrative office (e.g., accounting, HR, finance) |
AI Agent Use Cases and Applications
AI agents can analyze, perceive, learn, and make independent decisions. They are also able to adjust their strategies in response to changing environments, which makes them highly effective in fields that require flexibility and intelligent judgment.
Agentic AI, in turn, extends these capabilities by connecting AI agents with external tools and systems, enabling cross-platform collaboration and handling more complex, multidimensional tasks.
Below are some common examples showcasing how both AI agents and Agentic AI are applied across industries:
Examples of AI Agents:
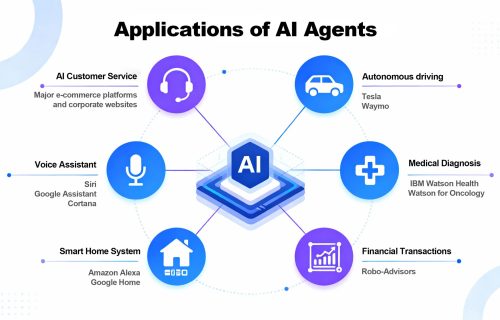
- Smart Customer Service Bots: Intelligent customer service agents can automatically respond to inquiries, provide real-time assistance, and guide users — a common feature across major e-commerce platforms and enterprise websites. Leveraging natural language processing (NLP), these agents understand customer intent and deliver accurate, context-based responses.
- Autonomous Driving Systems: Companies like Tesla and Waymo use AI agent technology at the core of their self-driving systems. By analyzing data from sensors and cameras, these agents perceive surroundings, make split-second decisions, and enable fully autonomous driving.
- Medical Diagnostic Assistance: In healthcare, AI agents are often used for analyzing patient records or interpreting medical images to assist doctors in diagnosis and treatment planning. A well-known example is IBM Watson Health, whose Watson for Oncology applies NLP to analyze patient data and medical literature, supporting oncologists in developing personalized treatment strategies.
Examples of Agentic AI:
- AI Voice Assistants: Applications like Siri, Google Assistant, and Cortana exemplify AI agents capable of understanding spoken commands, performing real-time searches, setting reminders, sending messages, and more. Over time, they learn user habits and preferences, improving their responsiveness and contextual accuracy.
- Smart Home Ecosystems: Solutions such as Amazon Alexa and Google Home integrate AI agent technology with external tools to manage smart devices — from lighting and speakers to curtains. Through automation rules and voice control, they can, for example, turn on the air conditioner and lights when a user arrives home, enhancing convenience and comfort.
- Financial Trading and Investment Advisory: In finance, Agentic AI systems like Robo-Advisors employ cross-system data analysis to recommend investment strategies. They automatically identify promising assets, design optimal portfolio allocations, and use quantitative models and time-series analysis to interpret market data (such as interest and exchange rates), helping investors reach their financial goals.
- Cybersecurity Protection: Agentic AI also plays a crucial role in cybersecurity. Automated threat detection and response systems can identify and react to attacks in real time to safeguard corporate data. For instance, UK-based Darktrace uses its “self-defending AI agent” Antigena, which autonomously isolates affected networks, enforces firewall rules, and restricts abnormal traffic once threats are detected.
The Future of AI Agents
As technology evolves, AI agents are no longer just auxiliary tools, they are reshaping how entire industries operate. From autonomous vehicles to intelligent customer service, AI agents are increasingly integrated into our daily work and life.
By understanding what AI agents are, their analytical frameworks, and how Agentic AI extends these capabilities, organizations can harness such technologies to streamline workflows and boost productivity.
If you’re looking to build your own AI agent system, OneAsia offers enterprise-grade data center hosting and computing services to help you deploy models efficiently, handle computation-intensive tasks, and dynamically scale processing power to support AI training, inference, and decision-making.
We also provide cloud services, known as cloud computing that automatically manage and adjust cloud resources based on your AI agent’s needs. When integrating multiple systems or managing large-scale cloud workloads, OneAsia’s cloud computing infrastructure ensures flexibility, scalability, and reliable support for AI agent deployment and operations.
As the technology continues to advance, AI agents are expected to create even greater value across industries by enhancing efficiency, minimizing human error, and inspiring new models of service and innovation.
To learn more about the latest developments in AI and our managed service offerings, contact OneAsia today.
References:
- 香港電腦學會文集 – 人工智能 Artificial Intelligence
- Google Cloud – 什麼是 Agentic AI?
- IBM Think – Agentic AI
- 遠見雜誌 GVM – 生成式 AI 進化為「代理型 AI」!比 ChatGPT 更強,能自主完成任務、協調多任務


