What Cybersecurity Risks Are Associated with Generative AI? An Overview of AI Data Security and Protection Methods
Blog / What Cybersecurity Risks Are Associated with Generative AI? An Overview of AI Data Security and Protection Methods
Have you ever considered that when you interact with an AI agent, the system may be learning your personal information while collecting and analyzing sensitive data that should be protected? The security risks hidden in the use of generative AI affect more than personal privacy. They may also impact business operations and regulatory responsibilities, making them a major topic in today’s AI security landscape.
This article from OneAsia walks you through the data security issues that may arise when applying AI and introduces protection methods so you can enjoy the convenience of AI while safeguarding your information.
What Are the Cybersecurity Risks of Generative AI?
According to a 2025 survey by the Hong Kong Office of the Privacy Commissioner for Personal Data (PCPD) involving 60 local organizations, 80% of the surveyed entities already use AI in their operations. Among them, 50% collect and use personal data through AI systems [1]. This shows that AI data security has become a critical concern in business operations.
Generative AI cybersecurity risks refer to the various security threats that can occur during the development, deployment and use of AI systems. Examples include prompt injection attacks that trick AI into revealing sensitive information, malicious attempts to modify model code, or manipulations that cause incorrect output. Since generative AI relies on continuous learning and model optimization, its decision-making process is often opaque and complex. This means sensitive data must be protected during training, while ensuring model integrity and overall system security.
Categories of Cybersecurity Risks in Generative AI
As generative AI evolves, international organizations have proposed different risk classifications, including NIST, OWASP, MITRE ATLAS and ENISA. Summarizing these perspectives, the cybersecurity risks of generative AI can be grouped into four major categories:
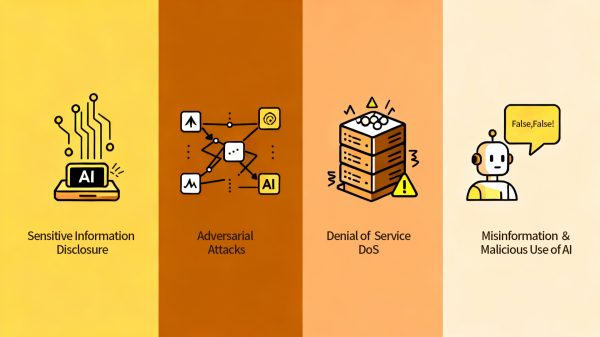
Sensitive Information Disclosure
Sensitive information disclosure is one of the most common AI security risks. It refers to unauthorized access, theft or exposure of private data such as personal identity information, medical records, financial details or corporate secrets.
In generative AI systems, these risks may originate from improper handling of training data or vulnerabilities within the system itself.
Adversarial Attacks
Adversarial attacks are another core risk in generative AI. Attackers may manipulate data or input malicious content that causes the AI model to misjudge or reveal sensitive information. Based on the MITRE ATLAS framework [2], common types of attacks include:
- Adversarial Examples: Small and almost undetectable changes to inputs that cause the model to make incorrect decisions. This includes subtle alterations to image pixels, audio waveforms or text.
- Prompt Injection: Embedding malicious instructions into input prompts or external resources to induce the model to violate its rules or expose private information.
- Data Poisoning: Injecting incorrect or malicious data during training or fine-tuning to damage the model’s accuracy and stability.
- Model Extraction/Theft: Repeatedly querying a model to collect input-output pairs, which an attacker can use to train a substitute model. If a company outsources AI model development to an unauthorized party, this may result in data security issues or even intellectual property loss.
- Model Inversion: Using model responses to infer the characteristics of training data and reconstruct private information.
Service Disruption (Denial of Service, DoS)
Generative AI requires significant computational resources for inference and training, including GPUs, network bandwidth and cloud infrastructure. Malicious or unexpected attacks may overwhelm these resources, causing degraded performance or complete service outages. This makes service disruption one of the most serious risks affecting operational stability. Common causes include:
- Query Flooding: Attackers send excessive requests, overloading the model and slowing or halting responses.
- API Abuse: Many generative AI systems are offered through APIs. Weak authentication can allow automated scripts to make large-scale calls, draining resources.
- Infrastructure Overload: In cloud or shared computing environments, attacks on CPU, memory or network bandwidth can push the system to its limits, preventing it from responding normally.
- Dependency or Supply-chain Attacks: Attacks targeting external platforms that AI models rely on, such as cloud providers, key management systems, third-party components or open-source packages. This can indirectly disrupt AI services and threaten the data security of companies that use AI in their operations.
Further reading: Infrastructure for Software Services: Understanding Cloud Service Models and Cloud Computing Deployment Models
Misinformation &Malicious Use of AI
Generative AI also brings risks related to fraud. In 2024, a widely reported case in Hong Kong involved an employee of a multinational company who was deceived during a video conference. Scammers used AI deepfake technology to fabricate both the visuals and the voice of senior staff, leading the employee to believe the instructions were legitimate. As a result, over HKD 200 million was transferred to multiple bank accounts.
This case highlights that beyond data leakage risks, generative AI may also be misused to create false information and content, potentially causing financial and operational damage.
Differences Between Traditional Cybersecurity Risks and AI Cybersecurity Risks
| Category | Traditional Cybersecurity Risks | AI Cybersecurity Risks |
|---|---|---|
| Attack target | Networks, databases and other conventional system resources | The AI model itself, training data and generated content |
| Predictability of behavior | Based on clear rules and easier to detect | Models learn and optimize, creating uncertainty in behavior |
| Nature of data sources | Usually structured attacks with identifiable origins | Large volumes of unstructured data with complex and varied sources |
| Scope of attack | Often focused on firewalls and network perimeters | Model APIs, third party models and external data sources |
Since traditional cybersecurity risks focus mainly on system and network protection, and generative AI risks involve models, data and algorithms across multiple layers, the potential attack surface becomes wider and the impact more difficult to predict. Safeguarding AI data security therefore requires more than strengthening infrastructure. It also needs to cover controls for model training processes, the use of third party models and the security of external resources.
AI Data Security and Protection Strategies
To address the various cybersecurity risks associated with generative AI, it is recommended to adopt a layered protection approach that enhances overall data and system security.
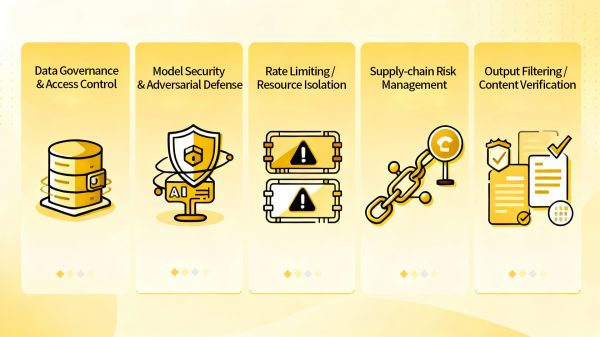
Data Governance & Access Control
Enterprises should classify and label different types of data (such as personal information, confidential business data and training datasets) and establish a clear authorization framework that ensures only permitted personnel can access or modify critical information. Measures such as encryption, secure transmission protocols like TLS/SSL and data access audit mechanisms should be implemented to prevent unauthorized access or data leakage.
Model Security & Adversarial Defense
To prevent the AI model from being misled or manipulated into making incorrect decisions, organizations should regularly test how the model performs when exposed to abnormal or malicious inputs. Early detection of vulnerabilities helps maintain AI data security. A continuous monitoring system should also be in place to track model behavior in real time and correct anomalies promptly.
Rate Limiting and Resource Isolation
Setting traffic limits and applying resource isolation helps reduce the risk of models being overwhelmed by high frequency queries or large scale API calls. Enterprises can define request limits based on user identity, use case or risk level, and deploy load balancing and abnormal traffic monitoring mechanisms to avoid service instability or security incidents.
Supply Chain and Third Party Risk Management
Modern AI systems often follow an agentic architecture that integrates external tools and third party services. All related resources require thorough security assessment. Regular checks on cloud platforms, open source components and third party packages help ensure compliance and prevent external threats from impacting core systems.
Further reading: What Are AI Agents? Understanding Their Analytical Capabilities and Applications
Output Filtering and Content Verification
A significant portion of generative AI risks arises from the model’s ability to create misleading or malicious content. To mitigate this, organizations should implement content filtering, output moderation and fact verification mechanisms to protect against misinformation and fraud. It is also recommended that any AI generated content be clearly labeled as such, allowing users to recognize the source of information.
Protecting AI Systems by Choosing a Trusted Platform

Generative AI introduces risks such as data leakage, model attacks, service outages and content abuse. Any of these can have long term effects on business operations and brand reputation. To strengthen AI data security, organizations should combine governance, technical safeguards and secure platforms through clear data management policies and reliable protection technologies.
OneAsia’s Security Operations Center (SOC) provides round the clock monitoring for AI systems, including model APIs, data access activities and cloud traffic. The SOC detects abnormal requests and potential attacks. Our cloud management service centralizes the management of AI applications and data, covering user permissions, encryption measures and API access controls. This ensures secure and traceable data transmission while effectively allocating computing resources to prevent service interruptions caused by high traffic or model workloads.
If you have any questions about secure AI deployment, feel free to contact OneAsia. We can help you build an AI ready infrastructure tailored for your organization.
References:
- PCPD – The Privacy Commissioner’s Office has Completed Compliance Checks on 60 Organisations to Ensure AI Security
- MITRE ATLAS – Techniques
- The Guardian – Company worker in Hong Kong pays out £20m in deepfake video call scam
- HKU Business School – AI騙案勢暴增 預防中伏靠AI
- HK01 – AI 的陰暗面:揭露新興的網絡安全威脅(蘇仲成)
- Ta Kung Wen Wei Media – 城大用AI拆解網騙作案手法
- Information Security Magazine Taiwan – 生成式 AI 時代的資安防禦策略


